How Can an Rfid Device Read Data From Several Credit Cards
What is RFID (radio frequency identification)?
RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the employ of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely place an object, animal or person.
How does RFID piece of work?
Every RFID arrangement consists of three components: a scanning antenna, a transceiver and a transponder. When the scanning antenna and transceiver are combined, they are referred to as an RFID reader or interrogator. There are 2 types of RFID readers -- stock-still readers and mobile readers. The RFID reader is a network-connected device that tin can be portable or permanently attached. It uses radio waves to transmit signals that actuate the tag. Once activated, the tag sends a wave back to the antenna, where information technology is translated into data.
The transponder is in the RFID tag itself. The read range for RFID tags varies based on factors including the type of tag, type of reader, RFID frequency and interference in the surrounding environment or from other RFID tags and readers. Tags that have a stronger power source also have a longer read range.
What are RFID tags and smart labels?
RFID tags are fabricated upwards of an integrated circuit (IC), an antenna and a substrate. The part of an RFID tag that encodes identifying information is called the RFID inlay.
There are two primary types of RFID tags:
- Agile RFID. An agile RFID tag has its own power source, often a battery.
- Passive RFID. A passive RFID tag receives its power from the reading antenna, whose electromagnetic moving ridge induces a current in the RFID tag's antenna.
There are also semi-passive RFID tags, meaning a battery runs the circuitry while communication is powered by the RFID reader.
Low-power, embedded not-volatile memory plays an of import office in every RFID arrangement. RFID tags typically hold less than ii,000 KB of information, including a unique identifier/series number. Tags can be read-only or read-write, where data tin be added by the reader or existing data overwritten.
The read range for RFID tags varies based on factors including blazon of tag, type of reader, RFID frequency, and interference in the surrounding environment or from other RFID tags and readers. Agile RFID tags have a longer read range than passive RFID tags due to the stronger power source.
Smart labels are uncomplicated RFID tags. These labels accept an RFID tag embedded into an agglutinative characterization and feature a barcode. They tin can also exist used by both RFID and barcode readers. Smart labels can be printed on-demand using desktop printers, where RFID tags crave more advanced equipment.

What are the types of RFID systems?
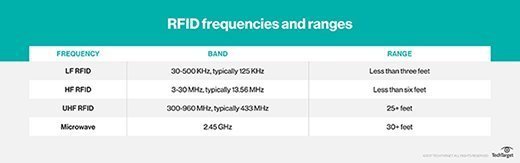
There are three master types of RFID systems: low frequency (LF), loftier frequency (HF) and ultra-high frequency (UHF). Microwave RFID is too bachelor. Frequencies vary profoundly past country and region.
- Depression-frequency RFID systems. These range from 30 KHzto 500 KHz, though the typical frequency is 125 KHz. LF RFID has curt transmission ranges, by and large anywhere from a few inches to less than vi feet.
- Loftier-frequency RFID organisation These range from 3 MHzto thirty MHz, with the typical HF frequency existence 13.56 MHz. The standard range is anywhere from a few inches to several feet.
- UHF RFID systems. These range from 300 MHz to 960 MHz, with the typical frequency of 433 MHz and tin can generally exist read from 25-plus feet abroad.
- Microwave RFID systems. These run at two.45 Ghzand tin can be read from 30-plus feet away.
The frequency used will depend on the RFID application, with actual obtained distances sometimes varying from what is expected. For instance, when the U.Due south. State Department announced it would issue electronic passports enabled with an RFID chip, information technology said the chips would only be able to be read from approximately 4 inches away. All the same, the State Section presently received evidence that RFID readers could skim the information from the RFID tags from much farther than 4 inches -- sometimes upward of 33 anxiety away.
If longer read ranges are needed, using tags with additional ability can boost read ranges to 300-plus feet.
RFID applications and utilise cases
RFID dates back to the 1940s; however, information technology was used more than frequently in the 1970s. For a long time, the high cost of the tags and readers prohibited widespread commercial use. As hardware costs accept decreased, RFID adoption has also increased.
Some common uses for RFID applications include:
- pet and livestock tracking
- inventory management
- asset tracking and equipment tracking
- inventory control
- cargo and supply chain logistics
- vehicle tracking
- customer service and loss control
- improved visibility and distribution in the supply chain
- access command in security situations
- shipping
- healthcare
- manufacturing
- retail sales
- tap-and-go credit carte du jour payments

RFID vs. barcodes
Using RFID as an alternative for barcodes is increasing in use. RFID and barcode technologies are used in similar ways to track inventory, simply there are some important differences betwixt them.
| RFID tags | Barcodes |
| Can identify private objects without straight line of sight. | Direct line of sight required for scanning. |
| Tin can scan items from inches to feet abroad, depending on type of tag and reader. | Require closer proximity for scanning. |
| Data can be updated in real time. | Information is read-merely and can't be changed. |
| Require a power source. | No power source needed. |
| Read time is less than 100 milliseconds per tag. | Read time is half a second or more than per tag. |
| Incorporate a sensor attached to an antenna, oftentimes independent in a plastic embrace and more costly than barcodes. | Printed on the exterior of an object and more discipline to article of clothing. |
RFID vs. NFC
Near-field advice (NFC) enables data to be exchanged between devices by using brusque-range, loftier-frequency wireless communication applied science. NFC combines the interface of a smart card and reader into a single device.
| Radio frequency ID | Near-field communication |
| Uni-directional | Bi-directional |
| Range upwardly to 100 m | Range less than 0.2 m |
| LF/HF/UHF/Microwave | xiii.56 MHz |
| Continuous sampling | No continuous sampling |
| Fleck charge per unit varies with frequency | Up to 424 Kbps |
| Power rate varies with frequency | <15 milliamperes |
RFID challenges
RFID is prone to two main issues:
- Reader collision. Reader standoff, when a bespeak from ane RFID reader interferes with a second reader, can be prevented by using an anti-collision protocol to brand RFID tags take turns transmitting to their advisable reader.
- Tag standoff. Tag standoff occurs when too many tags confuse an RFID reader by transmitting data at the same fourth dimension. Choosing a reader that gathers tag info ane at a time will prevent this issue.
RFID security and privacy
A common RFID security or privacy concern is that RFID tag data can exist read past anyone with a compatible reader. Tags tin often be read after an item leaves a shop or supply chain. They tin also be read without a user's knowledge using unauthorized readers, and if a tag has a unique serial number, it can be associated to a consumer. While a privacy business organization for individuals, in military or medical settings this can be a national security business concern or life-or-expiry matter.
Because RFID tags do not have a lot of compute power, they are unable to accommodate encryption, such as might exist used in a claiming-response authentication organisation. One exception to this, however, is specific to RFID tags used in passports -- basic admission control (BAC). Here, the chip has sufficient compute power to decode an encrypted token from the reader, thus proving the validity of the reader.
At the reader, information printed on the passport is machine-scanned and used to derive a primal for the passport. There are iii pieces of information used -- the passport number, the passport holder's nascence date and the passport'southward expiration date -- along with a checksum digit for each of the 3.
Researchers say this means passports are protected by a countersign with considerably less entropy than is normally used in e-commerce. They key is also static for the life of the passport, so once an entity has had one-time admission to the printed key data, the passport is readable with or without the consent of the passport bearer until the passport expires.
The U.S. State Department, which adopted the BAC system in 2007, has added an anti-skimming material to electronic passports to mitigate the threat of undetected attempts to steal users' personal information.
RFID standards
At that place are several guidelines and specifications for RFID technology, but the principal standards organizations are:
- International Arrangement for Standardization (ISO)
- Electronics Product Code Global Incorporated (EPCglobal)
- International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)
Each radio frequency has associated standards, including ISO 14223 and ISO/IEC 18000-2 for LF RFID, ISO 15693 and ISO/IEC 14443 for HF RFID, and ISO 18000-6C for UHF RFID.
Next-generation RFID use
RFID systems are becoming increasingly used to support cyberspace of things deployments. Combining the technology with smart sensors and/or GPS technology enables sensor data including temperature, motility and location to exist wirelessly transmitted.
Source: https://internetofthingsagenda.techtarget.com/definition/RFID-radio-frequency-identification
0 Response to "How Can an Rfid Device Read Data From Several Credit Cards"
Enregistrer un commentaire